If you’ve been wondering how to give your website a performance boost and climb higher in search engine rankings, look no further. Improving your website’s page speed is not as daunting as it sounds, and it can significantly enhance both your user experience and SEO results. From compressing images to leveraging browser caching, each small tweak you make can lead to quicker page loads and happier visitors. Dive in and discover practical tips and strategies to make your website faster and more efficient. Have you ever wondered why your website’s page speed matters so much for SEO? Well, you’re in the right place because we’re going to break down everything you need to know about improving your website’s page speed to boost your SEO.
Why Page Speed Matters
User Experience
Let’s kick things off with user experience. When people visit your website, they expect it to load quickly. If your pages take too long to load, visitors will likely click away and find what they’re looking for elsewhere. A slow website can frustrate users and leave a negative impression, which is not something you want.
Search Engine Rankings
Believe it or not, search engines like Google use page speed as a ranking factor. In fact, Google has been focusing on page speed for mobile searches since 2018. If your site is slow, it’s going to hurt your rankings. Faster pages are favored because they provide a better overall experience for users.
Diagnosing Your Current Page Speed
Tools to Use
Before you can fix the problem, you need to diagnose it. There are several tools out there that can help you identify how fast or slow your website is. Here are a few of the most popular ones:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Google PageSpeed Insights | Provides insights into mobile and desktop performance |
| GTmetrix | Offers detailed reports and analysis |
| Pingdom | Simplifies performance monitoring and offers grades based on speed |
| WebPageTest | Allows you to run tests from different locations |
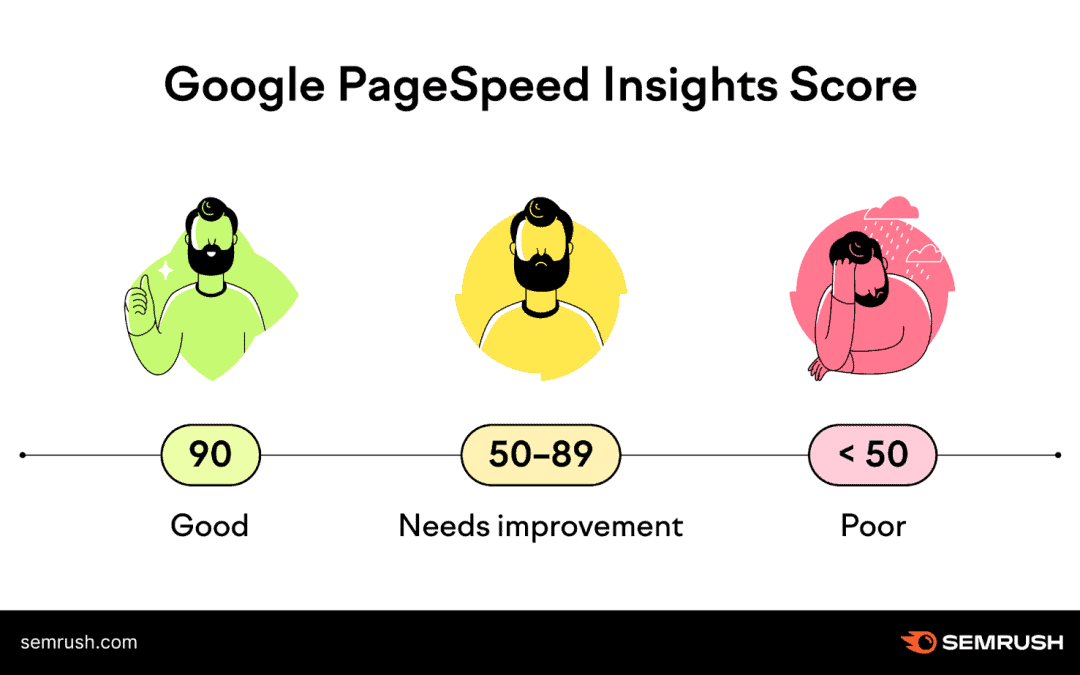
Google PageSpeed Insights is a favorite because it gives you a score based on how well your site performs and offers suggestions for improvement. Just type in your URL, and it will provide detailed information about what’s slowing down your page.
What Metrics to Look For
When you run a speed test, you’ll come across various metrics that might seem a bit confusing. Here are the key ones to pay attention to:
- First Contentful Paint (FCP): This tells you how long it takes for the first piece of content to appear on the screen.
- Speed Index: This shows how quickly content is visually displayed.
- Time to Interactive (TTI): The time it takes for the page to become fully interactive.
- Total Blocking Time (TBT): The amount of time that a page is blocked from responding to user input.
Understanding these metrics will help you know what needs to be improved.
How to Improve Page Speed
Optimize Images
One of the most common culprits of slow page speed is unoptimized images. High-resolution images are great, but they can slow down your site if not appropriately resized and compressed.
Resize and Compress
There are multiple ways to tackle this. You can manually resize images using tools like Adobe Photoshop or online options like TinyPNG and JPEGmini. Many Content Management Systems (CMS) offer plugins that can help automate this process.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| TinyPNG | Compresses PNG and JPEG images |
| JPEGmini | Reduces large JPEG images |
| Smush | A WordPress plugin for image compression |
| ImageMagick | A command-line tool for image processing |
Use the Right Formats
WebP and SVG formats are often better for web images than traditional JPEG or PNG formats. WebP offers better compression rates, and SVG works great for simple graphics like logos and icons.
Enable Browser Caching
When you enable browser caching, you’re telling visitors’ browsers to store some static files on their devices so they don’t have to download them every time they visit your site. This can significantly speed up page load times for repeat visitors.
You can manage browser caching through your .htaccess file if you’re on an Apache server. Just add the following lines:
ExpiresActive On ExpiresByType image/jpg “access 1 year” ExpiresByType image/jpeg “access 1 year” ExpiresByType image/gif “access 1 year” ExpiresByType image/png “access 1 year” ExpiresByType text/css “access 1 month” ExpiresByType text/html “access 1 month” ExpiresByType application/pdf “access 1 month” ExpiresByType text/javascript “access 1 month” ExpiresByType application/javascript “access 1 month” ExpiresByType application/x-shockwave-flash “access 1 month”
Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
Another technique for speeding up your website is minifying your code. This means removing unnecessary characters, including white spaces, comments, and line breaks, from your CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files.
Plugins and Tools
If you’re not a developer, don’t worry. There are various tools and plugins available for this purpose:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Minify | An online tool for manual minification of CSS and JavaScript |
| Autoptimize | A WordPress plugin that minifies CSS, JS, and HTML |
| UglifyJS | A JavaScript minification tool |
| CSSNano | A CSS minifier |
Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
A CDN helps by distributing your content across various servers around the world. This makes sure that users access your site from a server closest to them, reducing load times.
| CDN Provider | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloudflare | Offers both free and paid plans |
| Amazon CloudFront | Amazon’s fast, secure global CDN service |
| Akamai | One of the oldest and most reliable CDNs |
| Fastly | Known for its speed and real-time reporting |
Reduce Server Response Time
The time it takes for your server to respond to a request is another essential factor in page speed. If your server is slow, your page will be slow.
Upgrade Hosting Plans
Sometimes, the most straightforward solution is upgrading your hosting plan. If you’re on shared hosting, maybe it’s time to move to a VPS (Virtual Private Server) or even a dedicated server.
Use a Fast Database
A fast database can make a big difference. Make sure your database queries are optimized and always have your database indexed properly.
Advanced Techniques
Lazy Loading
Lazy loading means that images and other media only load when they come into the viewport. This reduces the initial load time and defers the loading of non-critical resources.
Prefetching and Preloading
These techniques let you load assets before a user needs them. Prefetching downloads pages that a user might navigate to next, while preloading loads assets needed for the current page.
Avoid Render-Blocking Resources
Render-blocking resources are files that a browser must load before it can render a web page. This includes CSS and JavaScript files. To avoid this, you can:
- Inline Critical CSS: Place essential CSS directly within the HTML document.
- Asynchronous Loading: Load JavaScript asynchronously using
asyncordeferattributes.
Track and Monitor
Regular Audits
Conduct regular speed audits using the tools we discussed earlier. This will help you stay on top of any issues that come up over time.
Set Alerts
Some tools like GTmetrix and Pingdom allow you to set alerts for when your page speed drops below a certain threshold. This can help you quickly identify and fix problems.
Conclusion
Improving your website’s page speed is not just about enhancing your SEO; it’s about providing a better user experience. Faster load times lead to happier visitors, which can result in higher conversion rates and better search engine rankings. While it might seem like a daunting task, the steps outlined above will give you a solid framework to work from. So, fire up those speed test tools and start optimizing today!
Further Reading
If you’re interested in diving deeper into any of these topics, here are some additional resources:
And that’s it! You’re now well-equipped to improve your website’s page speed, boosting both your user experience and SEO simultaneously. Happy optimizing!